Config file¶
The configuration file can be found anywhere but if the program runs in root mode, it is necessary that only root can modify the file. This is a security measure to prevent someone from executing commands as root using Amazon-dash.
To change the permissions:
sudo chmod 600 amazon-dash.yml
sudo chown root:root amazon-dash.yml
The amazon-dash system configuration file is located in: /etc/amazon-dash.yml
You can disable this security measure using --ignore-perms. Use this option at your own risk only in secure
environments (like Docker).
Important
Remember to restart the service whenever you make a change to apply it.
If you are using systemd, restart the service using systemctl restart amazon-dash
Example¶
The following example is available in /etc/amazon-dash.yml when installed:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
# On seconds. Minimum time that must pass between pulsations.
delay: 10
devices:
## Example of how to execute a system command
0C:47:C9:98:4A:12: # You can know the mac of your device with the discovery command
name: Kitcken button # You can put the name you want
user: your-user # System user. Necessary if it is executed as root
cmd: spotify # Command to execute
## Example of how to execute a system command over SSH
# AC:63:BE:75:1B:6F:
# name: Tassimo
# cmd: door --open
# ssh: 192.168.1.23:2222
## Example of how to execute a url
# AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1:
# name: Kit Kat
# url: 'http://domain.com/path/to/webhook' # Url to execute
# method: post # HTTP method. By default GET
# headers: {"authorization": "key"}
# content-type: json # Only available if Body is defined
# body: '{"mac": "AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1", "action": "toggleLight"}' # Request payload. Remember the quotes
## Example of how to execute a Homeassistant event
# 40:B4:CD:67:A2:E1:
# name: Fairy
# homeassistant: hassio.local # Address to the hass server
# event: toggle_kitchen_light # Event name to send
## Example of how to execute a Openhab event
# 18:74:2E:87:01:F2:
# name: Doritos
# openhab: 192.168.1.140 # Address to the openhab server
# item: open_door # Openhab item. Required
# state: "ON" # item state to send. TOGGLE by default
## Example of how to execute a IFTTT Webhook event
# 44:65:0D:75:A7:B2:
# name: Pompadour
# ifttt: cdxxx-_gEJ3wdU04yyyzzz
# event: pompadour_button
# data: {"value1": "Pompadour button"}
## Uncomment this for use confirmations
# confirmations:
## Example of how to send a Telegram confirmation on execution success or failure
# send-tg: # Confirmation name. Set your own confirmation name
# service: telegram # Confirmation service. Currently only Telegram
# token: '402642618:QwGDgiKE3LqdkNAtBkq0UEeBoDdpZYw8b4h' # Telegram token. Get it from Botfather
# to: 24291592 # Your Telegram id. You can get it using @get_id_bot
# is_default: true # Use by default this confirmation for all devices
# send-pb:
# service: pushbullet
# token: 'o.BbbPYjJizbPr2gSWgXGmqNTt6T9Rew51'
# is_default: false
# Need help? See the documentation:
# http://docs.nekmo.org/amazon-dash/config_file.html
# If you still need help open a issue:
# https://github.com/Nekmo/amazon-dash/issues
Real example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
0C:47:C9:98:4A:12:
name: Hero
user: nekmo
cmd: spotify
AC:63:BE:75:1B:6F:
name: Tassimo
cmd: door --open
ssh: 192.168.1.23:2222
AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1:
name: Kit Kat
url: 'http://domain.com/path/to/webhook'
method: post
content-type: json
body: '{"mac": "AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1", "action": "toggleLight"}'
confirmation: send-tg
40:B4:CD:67:A2:E1:
name: Fairy
homeassistant: hassio.local
event: toggle_kitchen_light
18:74:2E:87:01:F2:
name: Doritos
openhab: 192.168.1.140
item: open_door
state: "ON"
confirmation: send-pb
44:65:0D:75:A7:B2:
name: Pompadour
ifttt: cdxxx-_gEJ3wdU04yyyzzz
event: pompadour_button
data: {"value1": "Pompadour button"}
confirmations:
send-tg:
service: telegram
token: '402642618:QwGDgiKE3LqdkNAtBkq0UEeBoDdpZYw8b4h'
to: 24291592
is_default: false
send-pb:
service: pushbullet
token: 'o.BbbPYjJizbPr2gSWgXGmqNTt6T9Rew51'
is_default: false
Common options¶
The syntax of the configuration file is yaml. The configuration file has 3 main sections:
settings (optional): common options.
devices (required): The amazon dash devices.
confirmations (optional): confirmation on device executed.
settings section¶
The following options are available in settings:
delay (optional): On seconds. By default, 10 seconds. Minimum time that must pass between pulsations of the Amazon Dash button.
Device section¶
Each device is identified by the button mac. The mac can be obtained with the discovery command. In the configuration of each button, there may be a way of execution. Only one execution method is allowed for each device. The available exection methods are:
cmd: local command line command. Arguments can be placed after the command.
url: Call a url.
homeassistant: send event to Home Assistant. This argument must be the address to the hass server (protocol and port are optional. By default http and 8123, respectively).
openhab: send event to OpenHAB. This argument must be the address to the hass server (protocol and port are optional. By default http and 8080, respectively).
The devices can also have these common options:
name: device name for log messages.
confirmation: confirmation to use on device execution.
A device example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
0C:47:C9:98:4A:12:
name: Hero
user: nekmo
cmd: spotify
Confirmation section¶
Send a confirmation after running a device. Send a message whether the execution is successful or if it fails. If the execution returns an output this will be the message that is sent.
Each confirmation has a name to be able to use it on the devices (on the example confirmation-name):
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1:
name: Kit Kat
url: 'http://domain.com/path/to/webhook'
confirmation: confirmation-name
confirmations:
confirmation-name:
service: telegram
token: '402642618:QwGDgiKE3LqdkNAtBkq0UEeBoDdpZYw8b4h'
to: 24291592
For run a confirmation for all devices by default using is_default: true:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
# ...
confirmations:
confirmation-name:
service: telegram
token: '402642618:QwGDgiKE3LqdkNAtBkq0UEeBoDdpZYw8b4h'
to: 24291592
is_default: true
Execution¶
The devices section allows you to perform an action when you press an Amazon dash button. The following execution methods are available.
Execute cmd¶
When the cmd execution method is used, the following options are available.
user: System user that will execute the command. This option can only be used if Amazon-Dash is running as root.
cwd: Directory in which the command will be executed.
ssh: Optional. It allows executing the command on a remote machine.
Example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
0C:47:C9:98:4A:12:
name: Hero
user: nekmo
cmd: spotify
It is also possible to execute a command using SSH. The value of the ssh option must be the name/IP of the machine.
You can also specify the port. For example: machine:2222.
Example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
AC:63:BE:75:1B:6F:
name: Tassimo
cmd: door --open
ssh: 192.168.1.23:2222
Call url¶
When the url execution method is used, the following options are available.
method: HTTP method. By default GET.
headers: Headers to send to server. Content-Type will be overwritten if it is defined later.
content-type (*): HTTP Content-Type Header. Only available if Body is defined. If body is defined, default is form.
body: Request payload. Only if the method is POST/PUT/PATCH. In json or form mode, the content must be a valid json. It is recommended to use single quotes before and after content in json.
verify: By default True. Validate SSL/TLS certificate on request. To ignore errors (for example self-signed certificate) put false. You can also set the path to the certificate or certificate directory (generate using OpenSSL
c_rehashutility).
(*) Content type aliases: form = application/x-www-form-urlencoded. json = application/json.
plain =text/plain.
Example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1:
name: Kit Kat
url: 'http://domain.com/path/to/webhook'
method: post
content-type: json
body: '{"mac": "AC:63:BE:67:B2:F1", "action": "toggleLight"}'
confirmation: send-tg
Home Assistant event¶
When the homeassistant execution method is used, the following options are available.
event (required): Event name to send.
data: Event data to send. Use json as string.
access_token: Long-lived Home Assistant access token.
access: Home Assistant legacy API password (
x-ha-accessheader).verify: By default True. Validate SSL/TLS certificate on request. To ignore errors (for example self-signed certificate) put false. You can also set the path to the certificate or certificate directory (generate using OpenSSL
c_rehashutility). This can be useful if you use self-signed https.
Starting with version 0.78 of Home Assistant, there are two ways Amazon Dash can authenticate:
By providing a long-lived access token (generated within your Home Assistant profile page) via the
access_tokenoption.By providing the legacy Home Assistant API password via the
accessoption.
Although both options currently work, the Home Assistant project plans to deprecate (and likely remove) the legacy API password in the future; therefore, to properly future proof your Amazon Dash setup, the long-lived access token option is recommended.
The protocol and the port in the address of the Homeassistant server are optional. The syntax of the address is:
[<protocol>://]<server>[:<port>]. For example: ``https://hassio.local:1234.
Example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
40:B4:CD:67:A2:E1:
name: Fairy
homeassistant: hassio.local
event: toggle_kitchen_light
To perform the action in Home Assistant you can use any event name to send; for example, toggle_kitchen_light.
Then you must create an automation in Home Assistant to perform one or several actions in Home Assistant
when the event is received.
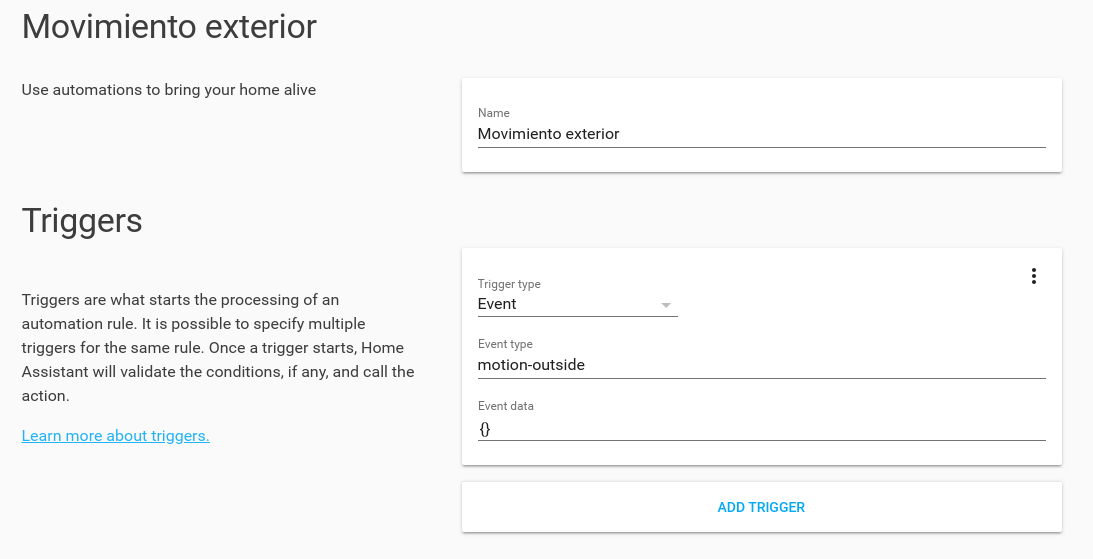
It is possible (but not recommended) to run a service directly using amazon-dash:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
40:B4:CD:67:A2:E1:
name: Fairy
homeassistant: hassio.local
event: call_service
data: '{"domain": "light", "service": "toggle", "service_data": {"entity_id": "light.Main_Room"}}'
Running a service using Amazon-dash is more limited and may break the configuration in the future. For example,
your entity_id could change in the future if you change your service.
More info in the homeassistant documentation:
OpenHAB event¶
When the openhab execution method is used, the following options are available.
item (required): Open Hab item to send.
state: State to send. On switch items ON/OFF. ON by default. The state must be between quotes.
The protocol and the port in the address of the OpenHAB server are optional. The syntax of the address is:
[<protocol>://]<server>[:<port>]. For example: ``https://192.168.1.140:1234.
Example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
18:74:2E:87:01:F2:
name: Doritos
openhab: 192.168.1.140
item: open_door
state: "ON"
IFTTT event¶
When the IFTTT execution method is used, the following options are available.
event (required): Event name to send. You define the event name when creating a Webhook applet.
data: dictionary with the “ingredients” (variables) for IFTTT.
To use IFTTT:
Create the applet by selecting the webhook service: https://ifttt.com/search . You will have to define a event name.
Get your IFTTT Webhook key: https://ifttt.com/services/maker_webhooks/settings
Put the event name and the key in the Amazon-dash configuration.
Example:
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
44:65:0D:75:A7:B2:
name: Pompadour
ifttt: cdxxx-_gEJ3wdU04yyyzzz
event: pompadour_button
data: {"value1": "Pompadour button"}
Confirmations¶
The following services are supported to send confirmation messages.
Telegram¶
For use a telegram service you need to define:
token: get your own token for your bot using
/newboton @BotFather.to: your telegram id. You can get it using @get_id_bot or other method.
After create a bot, you need to start a conversation with your bot. Bots can not send messages to users if people have not started a conversation before.
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
# ...
confirmations:
send-tg:
service: telegram
token: '402642618:QwGDgiKE3LqdkNAtBkq0UEeBoDdpZYw8b4h'
to: 24291592
is_default: false
Pushbullet¶
For use a pushbullet service you need to define:
token: Get it in your pushbullet Access Token (create a token): https://www.pushbullet.com/#settings/account
Optional: set a target (you can only set a target):
device_iden: Device identifier. To get your device identifier:
$ curl --header 'Access-Token: <YOUR TOKEN>' https://api.pushbullet.com/v2/devicesemail: Useful to send a message to your contacts.
channel_tag: Send to all subscribers to your channel.
client_iden: Send to all users who have granted access to your OAuth client.
# amazon-dash.yml
# ---------------
settings:
delay: 10
devices:
# ...
confirmations:
send-pb:
service: pushbullet
token: 'o.BbbPYjJizbPr2gSWgXGmqNTt6T9Rew51'
is_default: false



